Learning Outcomes:
i. Students will grasp the method of determining an object's density using Archimedes' principle.
ii. Comprehend the relationship between the weight of an object in air and its weight when submerged in a fluid, providing a means to calculate density.
iii. Recognize the significance of volume in determining density, understanding that density is a measure of mass per unit volume.
iv. Apply the equation ρ = (W_air - W_fluid) / V to calculate the density of various objects using Archimedes' principle.
v. Appreciate the practical applications of density determination in various fields, such as material identification and purity assessment.
Introduction:
As we encounter objects of diverse materials and shapes, we often wonder about their composition and how they interact with their surroundings. The concept of density, a fundamental property of matter, provides a key to understanding these interactions. Density, defined as mass per unit volume, reflects the compactness of a material and its behavior in various environments. In this lesson, we explore the ingenious method of determining density using Archimedes' principle, a technique that harnesses the buoyant force exerted on submerged objects.
i. The Weight Paradox: A Tale of Two Environments
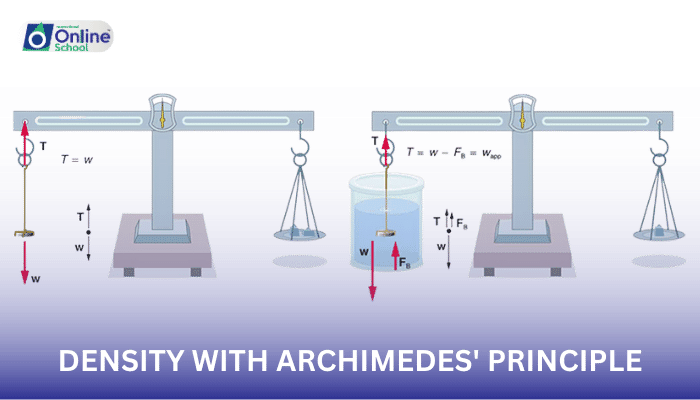
When an object is weighed in air, we measure the force of gravity acting on its mass. However, when the same object is submerged in a fluid, it experiences an upward force known as buoyancy, which counteracts its weight. This difference in weight, when compared to the weight in air, provides valuable clues about the object's density.
ii. Archimedes' Principle: A Density-Revealing Force
Archimedes' principle states that the buoyant force exerted on an object submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. This principle suggests that by measuring the difference in weight of an object in air and when submerged in a fluid, we can determine the volume of the fluid displaced.
iii. Volume: A Key to Density Determination
The volume of the fluid displaced by an object is a crucial parameter in calculating its density. This volume represents the space occupied by the object in the fluid and provides a measure of the object's compactness.
Calculating Density: A Formula to Unveil the Secrets
The density of an object using Archimedes' principle can be calculated using the equation:
ρ = (W_air - W_fluid) / V
where:
- ρ is density (in kilograms per cubic meter)
- W_air is weight of the object in air (in Newtons)
- W_fluid is weight of the object submerged in a fluid (in Newtons)
- V is volume of the fluid displaced by the object (in cubic meters)
iv. Real-World Applications: Density Determination in Action
The method of determining density using Archimedes' principle has numerous practical applications:
Material Identification: Identifying unknown materials based on their density, aiding in material selection and quality control.
Purity Assessment: Assessing the purity of substances, such as metals, by comparing their measured density to the theoretical density of the pure material.
Volume Calculation: Determining the volume of irregularly shaped objects by measuring their weight in air and submerged in a fluid.
Archimedes' principle, a cornerstone of fluid mechanics, provides an elegant and practical method for determining the density of various objects. By understanding the relationship between weight, volume, and buoyancy, we can unlock the secrets of density, a fundamental property of matter that governs its interactions and behaviors in our physical world. As we explore the diverse applications of density determination, we appreciate the ingenuity of Archimedes' principle and its enduring impact on scientific and technological advancements.